In this guide, we’ll explain the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 EV chargers. We’ll also discuss their pros and cons, factors to consider when choosing the right charger, and compare both options in terms of cost.
The different levels of EV charging
The charging speed of a vehicle is determined by the charging power. Basically, an increased level corresponds to a higher charging current, resulting in a quicker charging process for the car.
The primary levels of EV charging are Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. In this article, we’ll only focus on Levels 1 and 2 because they are the most practical and commonly used for homes and businesses.
Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations differ in their charging speeds, power requirements, and installation processes. Knowing the differences will help you determine which charging station best suits your needs, whether you’re looking for a residential or commercial solution.
Understanding the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers
Level 1 Chargers: a quick overview
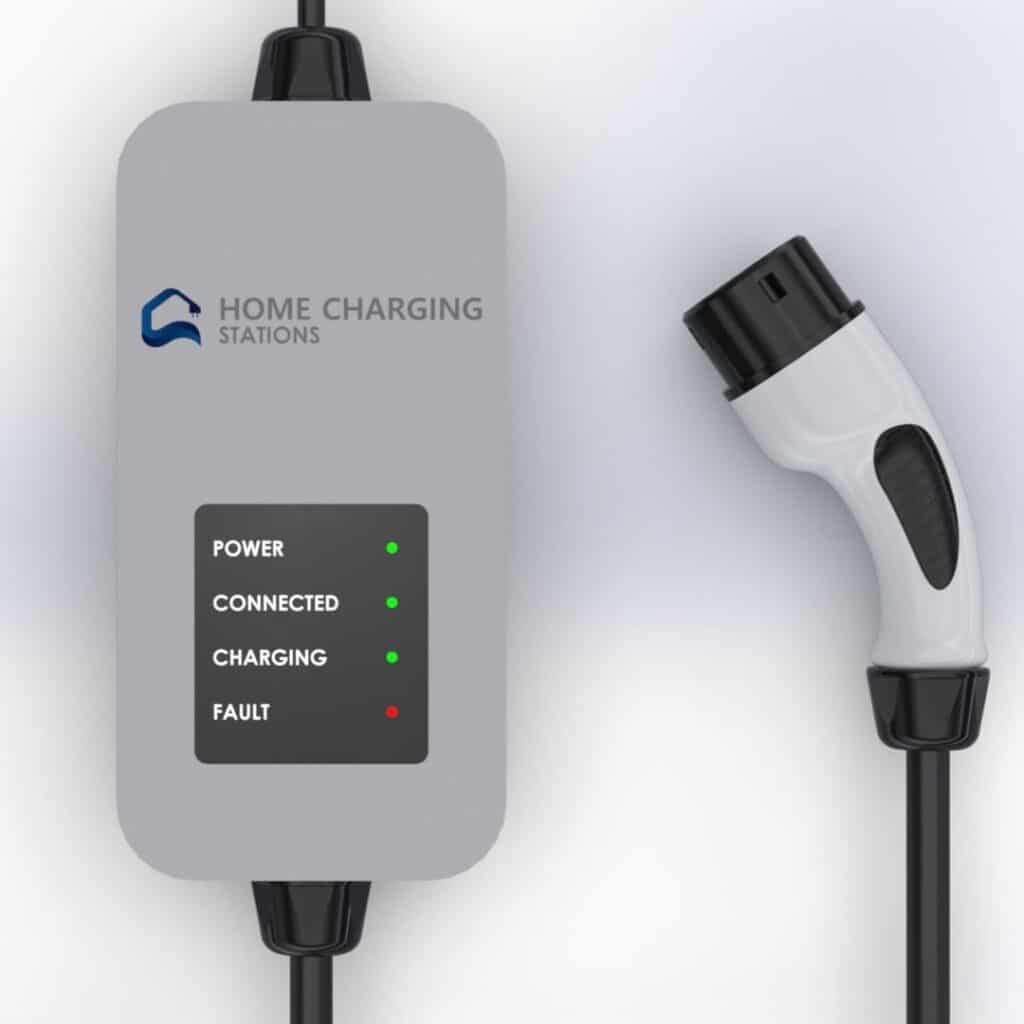

Level 1 chargers use a standard 120-volt (V) US household electrical outlet (NEMA), making them the most accessible and straightforward option for charging an electric vehicle (EV). Level 1 charging can be done using the EV’s factory-provided charging cable, which typically includes a standard three-prong plug for the outlet and a connector for the vehicle’s charging port. A Level 1 charger is capable of charging an electric vehicle with a power range of 1.4 kW to 1.9 kW.
Level 2 Chargers: a quick overview
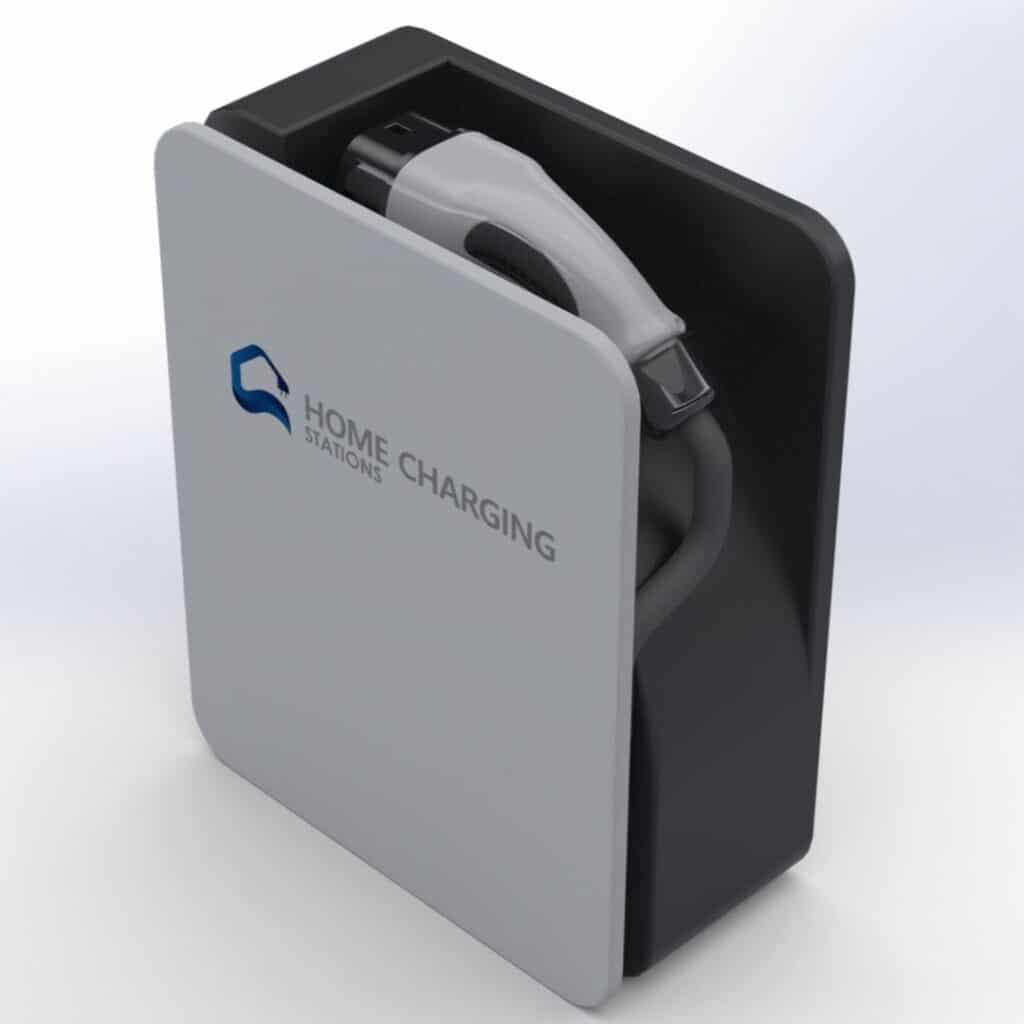

Level 2 charging stations also use the 240-volt electrical supply of the house, similar to the power used by household appliances like electric dryers and ovens. They require a dedicated charging cable and connector, which are typically provided for the installation of the charging station.
Level 1 vs Level 2 charging: key differences
During our research, we came across an interesting report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) confirming that the main difference between these two chargers is the voltage used during charging, as mentioned earlier.
From our experience, a few other practical aspects should be considered when comparing both Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations:
- Charging time
- Installation
- Price
- Mobility
- Safety
1. Charging Time
The primary difference between level 1 and level 2 charging stations is their charging speed. Level 2 stations offer faster charging due to higher current, making them ideal for EV owners with larger batteries or frequent charging needs.
Level 1 chargers provide 2-5 miles of range per hour (RPH) and may be suitable for short commutes or charging at work. Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, provide 10-60 miles of range per hour, making them a popular choice for those with longer commutes, road trips, or seeking faster home or workplace charging.
Check out our electric vehicle charging time calculator to determine the time you would need to charge any car with the charging station of your choice.
2. Installation
Another key difference between Level 1 and Level 2 chargers is their installation requirements. Level 1 chargers are simply plugged into an existing outlet using a common Nema 5 plug, while Level 2 stations require a dedicated circuit and often professional installation. Many Level 2 chargers can be plugged in using a Nema 14-50 plug.
3. Price
The cost of Level 1 and Level 2 chargers also differs significantly. Level 1 chargers are generally more affordable, as they do not require any specialized equipment or installation services. In contrast, Level 2 charging stations have a higher upfront cost and may require additional expenses for installation and electrical work.
Please find below a comprehensive infographic we’ve created comparing the main differences between Level 1 and Level 2 chargers.
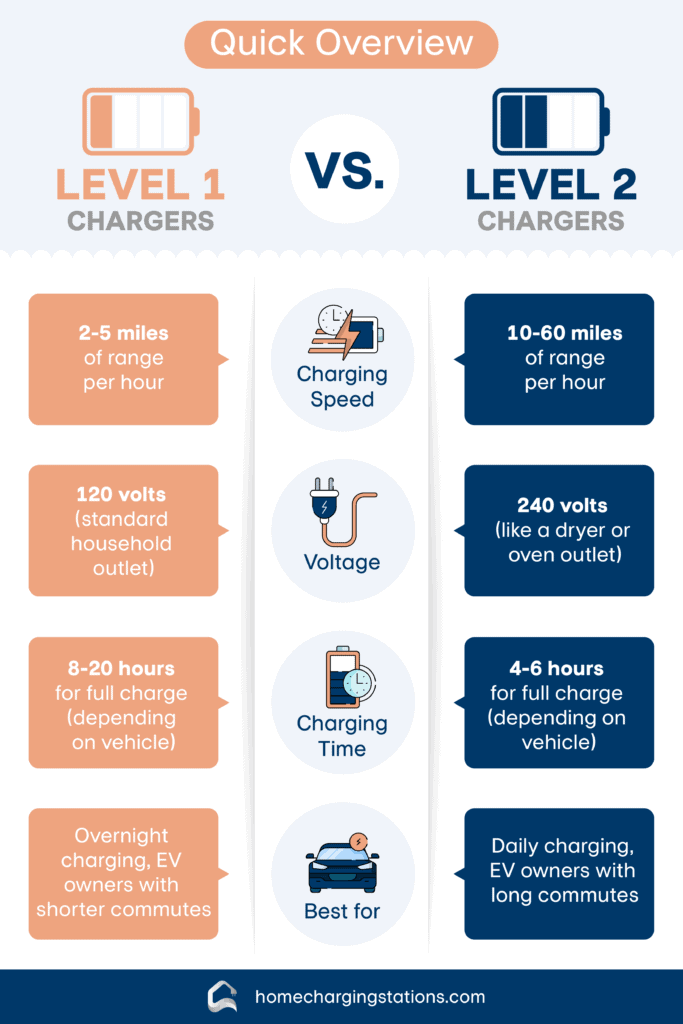
4. Mobility
Mobility should also be taken into consideration. Level 1 chargers can be easily carried wherever and whenever you want, which is quite convenient. However, not all level 2 chargers are portable since most of them are wall-mounted and cannot be transported.
5. Security
You might also wonder if both levels are equal regarding security. We did some research on this topic and the simple answer is, yes. Both Level 1 and Level 2 chargers are manufactured with a safety switch. Electric car chargers are weatherproof and are specifically designed to protect both the car and people from electric sparking or shocks.
Here’s a summary of the differences between Level 1 and Level 2 charging that we just discussed:
| Characteristics | Level 1 Charger | Level 2 Charging Station |
|---|---|---|
| Charging time for 100 miles or km | Slow – 10.5 hours with a 1.9kW charger for 100 miles (or km) for a 20kWh consumption per 100 miles or km | Fast – 1.8 hours with an 11kW charger for 100 miles (or km) for a 20kWh consumption per 100 miles or km |
| Full charging time | 31.6 hours for a 60kW EV battery with a 1.9 kW charger | 5.5 hours for a 60kW EV battery with an 11 kW charger |
| Rough max. power | About 1.9 kW | Between 3.4 and 22 kW |
| Price | Free – Provided with the electric car | Between $300 (€) and $1000 (€) on average + Installation cost |
| Installation | Can be installed by anyone who might not be familiar with electric equipment | Requires proper installation by yourself or by a qualified electrician |
| Mobility | Can be easily carried out wherever you want in the trunk of your car | Most of them are wall-mounted and can’t be transported |
| Safety switch | Yes | Yes |
| Weatherproof | Yes | Yes |
We’ve compiled a list of pros and cons for both Levels.
Pros and cons of Level 1 charging
Pros:
- Low upfront cost: Level 1 chargers are cheaper and do not require any specific equipment or installation services, making them an affordable option for EV owners.
- Ease of installation: Level 1 charger can be easily set up using an existing 120V electrical outlet.
- Universal compatibility: Level 1 chargers are compatible with all-electric vehicles, making them a versatile charging solution.
Cons:
- Slow charging speed: Level 1 chargers offer slower charging speeds compared to Level 2 charging stations, which can be inconvenient for EV owners who require faster charging.
- Limited range per hour of charging: Level 1 charging stations provide a limited amount of electric range per hour of charging, which may not be sufficient for those with longer commutes or limited charging time.
Pros and cons of Level 2 charging
Pros:
- Faster charging speed: Level 2 chargers offer faster charging times as compared to Level 1 chargers. This makes them an efficient and convenient choice for electric vehicle owners.
- Greater range per hour of charging: Level 2 charging stations offer a higher electric range per hour of charging, making them more suitable for those with longer commutes or limited charging time.
- Increased home value: Installing a Level 2 charging station at home can increase the property’s value and appeal to potential buyers who own or are considering purchasing an electric vehicle.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: Level 2 charging stations have a higher upfront cost compared to Level 1 chargers, due to the need for additional equipment and installation services.
- More complex installation: Level 2 charging stations require a dedicated 240V electrical circuit and professional installation, which can be more time-consuming and costly compared to Level 1 chargers.
Factors to consider when choosing a charging station
We recommend considering the following factors when choosing a charger:
- Charging speed: If you require a faster charging time or have limited time to charge your vehicle, Level 2 charging stations may be the better option.
- Upfront cost and installation: Consider your budget and the potential expenses associated with installing a Level 2 charging station, including the cost of the equipment and any necessary electrical work.
- The daily commute and driving habits: If you have a shorter daily commute or access to charging stations at work, Level 1 chargers may be sufficient for your needs.
- Future-proofing: As electric vehicle technology continues to advance, it may be beneficial to invest in a Level 2 charging station to accommodate potential increases in charging speed and battery capacity.
Cost comparison: Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations
The cost of Level 1 and Level 2 chargers varies significantly due to the differences in equipment, installation, and electrical requirements.
Level 1 chargers are usually provided by the manufacturer of the electric vehicle at no extra cost.
On the other hand, the price of a Level 2 charging station varies between $300 and $1000, based on the brand and type. Additionally, installation expenses could vary between $500 to $2000, based on the complexity of the task.
While the upfront cost of Level 2 chargers may be higher, the long-term benefits of faster charging speeds and increased electric range may outweigh the initial investment for many EV owners.
Installation process for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers
The installation process for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers differs significantly due to their varying power requirements and equipment needs.
EV owners can easily plug their Level 1 charger into an existing 120V electrical outlet. It’s essential to make sure that the outlet is in good condition and capable of handling the constant load of charging an EV.
Level 2 charging stations require a dedicated 240V electrical circuit, which often necessitates the services of a professional electrician for installation. The installation process typically involves the following steps:
- Electrical inspection: A licensed electrician will assess the electrical panel and determine if the existing electrical service can accommodate the new circuit and charging station.
- Circuit installation: If the electrical service is sufficient, the electrician will install a dedicated 240V circuit for the charging station, which involves running new wiring from the electrical panel to the charging location.
- Mounting the charging station: The charging station will be mounted by the electrician after installing the circuit. They will also connect it to the circuit and test it for proper functioning and safety.
- Testing: The electrician will test the charger to ensure it is functioning correctly and safely.
The steps above will ensure that the installation is done correctly to avoid any potential safety risks.
Our personal recommendations
As always, there is no right or wrong. We highly recommend always carrying your Level 1 charger in your car. Even with improving infrastructure, it’s reassuring to know that we can charge almost anywhere, and all we need is a common plug. We’ve asked a few EV owners, and they completely agree with this.
If you have a dedicated parking spot and are able to mount a charging station, it is a great feeling to know, that you have a fully charged car the next morning.
If you’re not certain about the Level of charger you require, we suggest testing a Level 2 charger first before purchasing one. You might find it useful to explore some companies that offer leasing options to assess your charging habits.
Conclusion: Which Charging Station is Right for You?
Level 1 and Level 2 chargers can be both great options depending on your needs, especially if you want to enjoy the benefits of charging at home.
A wise decision relies on your choices, flexibility, time availability, cost approach, and familiarity with electrical equipment. Therefore, keep in mind all these scenarios and then opt for one out of these two.
If you have any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us at contact@homechargingstations.com.
